A major impediment to in-depth study of African languages is the absence of metalanguages for studying them in schools. This consciousness has elicited a patriotic response from concerned Igala linguists and ‘linguistic engineers,’ who have come together to lay a foundation for the scientific study of Igala language, starting with creating a metalanguage that will facilitate learning. Their first preoccupation was the coinage for the English word, ‘grammar,’ as Ọ̀kpàkpà-Ùkọ̀là (Correct Use of Words). Based […]
The Igala Alphabet
P.A. Ogundipe, C.E. Eckersley and M. Macaulay, co-authors of Brighter Grammar Book 1 (1983), define grammar as ‘the art of putting words in the right places.’ Igala language is richly-structured; and it is spoken with relish and a sense of national pride, In spite of its verbal fluency and poetry, the language is yet to be sufficiently described, as evidenced by the conspicuous absence of an effective Igala equivalent for the English word, ‘grammar,’ hence, […]
A HISTORY OF TWO MONARCHIES
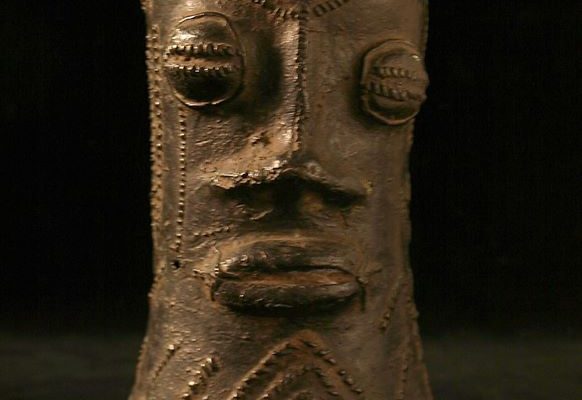
Igala History: Áyẹ́gbà Ọma Ìdoko The biography of Àtá Áyẹ́gbà Ọma Ìdoko is anchored on both oral and written claims by different sources. Oral history has it that his mother was called Ífùnányá and that she hailed from Énúgu Ezìkè, an Ìgbò community across the eastern border where, for over five hundred years, the Igala have had a commanding presence. On his father’s side, he descended from the Àbùtù Ẹ̀jẹ̀ […]
Numbers Pool – Álúkà
Historical Background Since the beginning of time, the Ígáláà have evolved a system of counting that stretches to large numbers beyond the imagination of the modern Igala youths and adults. Through this ancient system, Igala ancestors, who were predominantly farmers, were able to take record of their properties: the heaps they constructed in one day, the harvest of yam tubers, sacks of grains, and, of course, the cowries earned at the end of a market […]
Parts of Speech: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can function by itself as a noun phrase and that refers either to the participants in the discourse (e.g., I, you ) or to someone or something mentioned elsewhere in the discourse (e.g., she, it, this ). In the Igala language, there are [insert text here]… NÀ ÒMÌ, U; ÙWẸ̀, Ẹ̀; ÀWÀ (à) or À; ÀMÀ, MÀ; I, ÒÑWÙ; ÑWU Sometimes, you choose not to mention nouns. Instead, you use other words in their places. Those ‘other words’ are […]